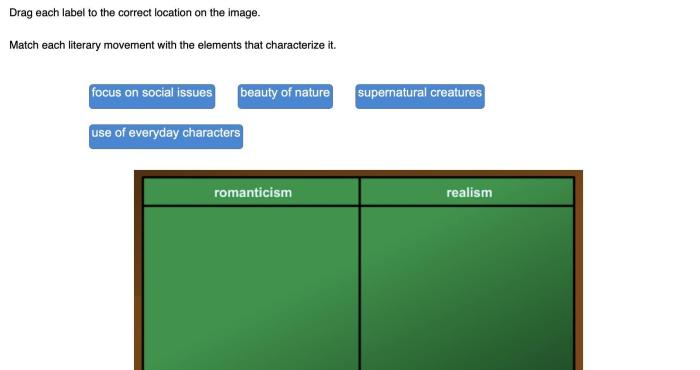
Match each literary movement with the elements that characterize it. – In the realm of literature, various movements have emerged, each characterized by distinct elements. From Romanticism’s emphasis on emotion and individualism to Postmodernism’s critique of traditional notions, this exploration delves into the defining features of these literary movements.
Throughout history, literary movements have challenged prevailing norms and expanded the boundaries of artistic expression. By examining the key elements that characterize each movement, we gain insights into the motivations, beliefs, and influences that shape literary works.
Romanticism
Romanticism, a literary movement that emerged in the late 18th century, emphasized the importance of emotion, imagination, and individualism. It challenged the Enlightenment’s emphasis on reason and logic, instead embracing the power of imagination and the beauty of nature.
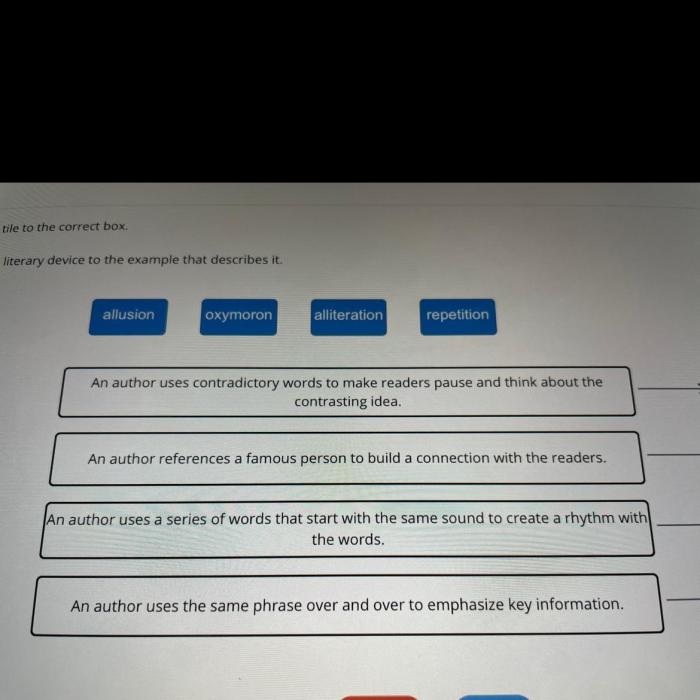
Emphasis on Emotion
Romanticism placed a strong emphasis on the expression of emotions, particularly those that were intense and passionate. Writers explored the depths of human emotion, delving into themes of love, loss, and longing. They believed that emotions were essential to understanding the human experience and that literature should capture the full range of human feelings.
Imagination as a Source of Truth
Romantics believed that imagination was a powerful tool that could reveal truths that reason could not. They rejected the Enlightenment’s emphasis on objective reality, instead embracing the subjective and imaginative experiences of the individual. Imagination allowed writers to explore the unknown, the fantastic, and the mysterious, opening up new possibilities for literary expression.
Individualism and the Importance of the Self
Romanticism celebrated the individual and the importance of self-expression. Writers focused on the unique experiences and perspectives of individuals, exploring the complexities of the human psyche. They believed that each person had a unique voice and that literature should reflect the diversity of human experience.
Nature as a Source of Inspiration
Nature played a significant role in Romantic literature, serving as a source of inspiration and a symbol of the human spirit. Romantic writers found beauty and solace in the natural world, seeing it as a reflection of their own inner emotions and experiences.
They believed that nature could inspire creativity and provide insights into the human condition.
Realism

Realism, a literary movement that emerged in the mid-19th century, focused on depicting everyday life and ordinary people. It challenged the idealized and romanticized depictions of life in previous literary movements, instead embracing a more objective and accurate portrayal of reality.
Depiction of Everyday Life
Realists aimed to capture the真实生活of everyday people, focusing on their struggles, joys, and mundane experiences. They believed that literature should reflect the真实生活of the majority of the population, rather than focusing on the lives of the wealthy and privileged.
Objective Observation and Detailed Descriptions
Realists used objective observation and detailed descriptions to create a sense of authenticity in their writing. They avoided exaggeration and sentimentality, instead striving to present life as it was, without embellishment. They believed that by accurately depicting the details of everyday life, they could provide readers with a deeper understanding of the human condition.
Focus on Ordinary People
Realists focused on the experiences of ordinary people, rather than heroes or extraordinary individuals. They believed that the lives of everyday people were just as worthy of exploration as the lives of the famous and powerful. By depicting the struggles and triumphs of ordinary individuals, Realists aimed to shed light on the universal human experience.
Modernism
Modernism, a literary movement that emerged in the early 20th century, was characterized by experimentation with form, language, and structure. It challenged traditional narrative techniques and embraced fragmentation and ambiguity, reflecting the changing social and intellectual landscape of the time.
Experimentation with Form
Modernists experimented with a variety of literary forms, breaking away from traditional structures and conventions. They used stream-of-consciousness, interior monologues, and multiple perspectives to explore the complexities of the human mind. They believed that traditional forms were too restrictive and that new forms were needed to capture the complexities of modern life.
Fragmentation and Ambiguity
Modernists embraced fragmentation and ambiguity, rejecting the idea of a single, unified narrative. They believed that reality was often fragmented and ambiguous, and that literature should reflect this complexity. They used multiple perspectives, unreliable narrators, and non-linear timelines to create a sense of disorientation and uncertainty.
Exploration of the Human Mind
Modernists were deeply interested in exploring the complexities of the human mind. They used stream-of-consciousness and interior monologues to capture the inner thoughts and feelings of their characters. They believed that the human mind was a vast and unexplored territory, and that literature could provide insights into its workings.
Postmodernism
Postmodernism, a literary movement that emerged in the mid-20th century, critiqued traditional notions of truth, reality, and objectivity. It embraced diversity and fragmentation, challenging the idea of a single, unified narrative.
Critique of Traditional Notions of Truth and Reality
Postmodernists rejected the idea of a single, objective truth. They believed that truth was subjective and that there were multiple perspectives on any given issue. They also questioned the concept of reality, arguing that it was constructed by social and cultural forces.
Embrace of Diversity and Fragmentation
Postmodernists celebrated diversity and fragmentation, rejecting the idea of a single, unified narrative. They believed that there were multiple perspectives on any given issue and that no one perspective could claim to be the only true one. They embraced fragmentation and discontinuity, seeing them as reflections of the complex and multifaceted nature of reality.
Use of Metafiction, Intertextuality, and Irony, Match each literary movement with the elements that characterize it.
Postmodernists used metafiction, intertextuality, and irony to question and subvert established norms. Metafiction refers to the use of literary devices to call attention to the artificiality of fiction. Intertextuality refers to the incorporation of other texts into a new work, creating a sense of interconnectivity and undermining the idea of originality.
Irony is used to create a sense of detachment and distance, allowing readers to question the validity of the text and the world it presents.
Key Questions Answered: Match Each Literary Movement With The Elements That Characterize It.
What is the significance of literary movements?
Literary movements provide a framework for understanding the evolution of literary styles and themes, reflecting the social, cultural, and intellectual currents of their time.
How do literary movements influence literary works?
Literary movements shape the form, content, and perspective of literary works, guiding authors’ choices of language, narrative techniques, and subject matter.
What are some key elements to consider when identifying a literary movement?
Elements such as emphasis on emotion, depiction of everyday life, experimentation with form, and critique of established norms can help identify the defining characteristics of a literary movement.