Small hair like structures used for movement or sensing things – Small hair-like structures, known as cilia, flagella, microvilli, stereocilia, and sensory hairs, play crucial roles in movement and sensing throughout the animal kingdom. These minute projections extend from cell surfaces, exhibiting diverse structures and functions that contribute to locomotion, sensory perception, and various physiological processes.
From the coordinated beating of cilia lining respiratory tracts to the whip-like propulsion of flagella driving sperm cells, these structures demonstrate the remarkable diversity and adaptability of cellular components.
Small Hair-Like Structures Used for Movement or Sensing Things
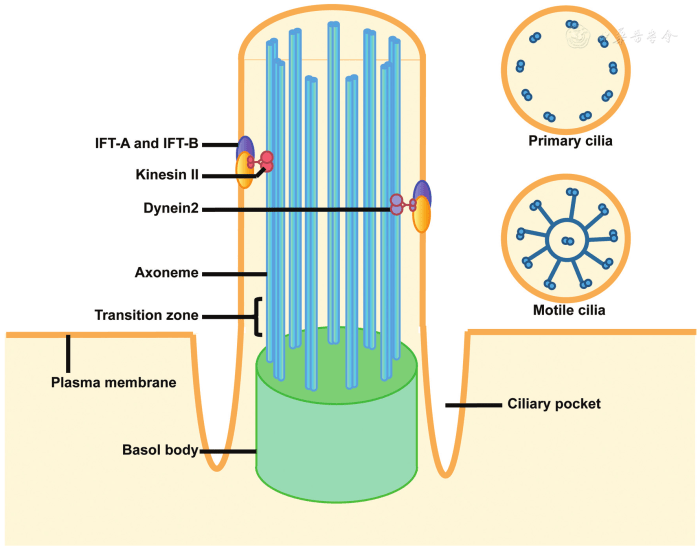
Small hair-like structures are found on the surface of many cells in the body. These structures, which are typically made of microtubules, are involved in a variety of functions, including movement and sensing things.
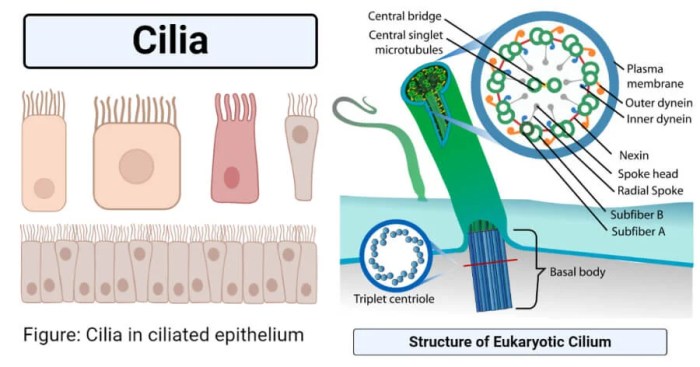
Cilia
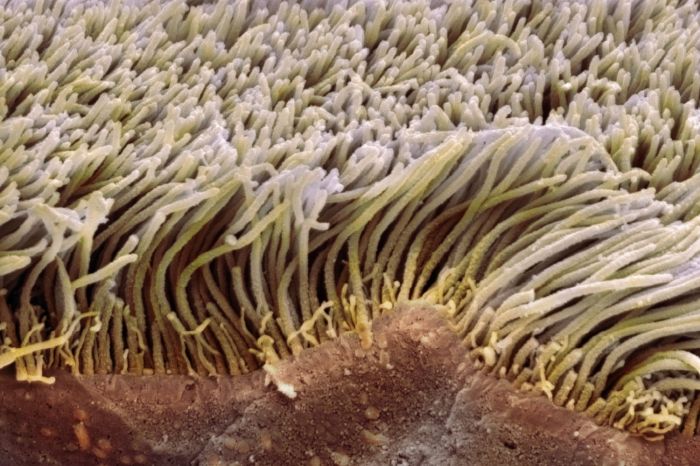
Cilia are short, hair-like structures that are found on the surface of many cells. They are typically between 5 and 10 micrometers in length and are composed of microtubules. Cilia beat in a coordinated manner, which helps to move fluid or mucus over the surface of the cell.
Cilia are found in a variety of organisms, including humans, animals, and plants. In humans, cilia are found in the respiratory tract, where they help to move mucus out of the lungs. Cilia are also found in the female reproductive tract, where they help to move eggs towards the uterus.
Flagella
Flagella are long, whip-like structures that are found on the surface of some cells. They are typically between 10 and 100 micrometers in length and are composed of microtubules. Flagella beat in a whip-like manner, which helps to propel the cell through fluid.
Flagella are found in a variety of organisms, including bacteria, protozoa, and some animals. In bacteria, flagella help to propel the cell through fluid. In protozoa, flagella help to move the cell towards food or away from danger. In some animals, flagella help to propel the animal through water.
Microvilli
Microvilli are small, finger-like projections that are found on the surface of some cells. They are typically between 1 and 2 micrometers in length and are composed of microfilaments. Microvilli increase the surface area of the cell, which helps to increase the rate of absorption or secretion.
Microvilli are found in a variety of cells, including intestinal cells, kidney cells, and lung cells. In intestinal cells, microvilli help to absorb nutrients from food. In kidney cells, microvilli help to filter blood. In lung cells, microvilli help to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Stereocilia
Stereocilia are long, hair-like structures that are found on the surface of some cells in the inner ear. They are typically between 10 and 100 micrometers in length and are composed of microtubules. Stereocilia are arranged in rows, and they are connected to each other by tip links.
Stereocilia are involved in hearing and balance. When sound waves enter the inner ear, they cause the stereocilia to bend. This bending triggers an electrical signal that is sent to the brain, which interprets the signal as sound.
Sensory Hairs, Small hair like structures used for movement or sensing things
Sensory hairs are long, hair-like structures that are found on the surface of some cells in the skin and other organs. They are typically between 10 and 100 micrometers in length and are composed of keratin. Sensory hairs are sensitive to touch and pressure, and they help to transmit sensory information to the brain.
Sensory hairs are found in a variety of animals, including humans, cats, and dogs. In humans, sensory hairs are found on the skin, the tongue, and the inside of the nose. In cats, sensory hairs are found on the whiskers.
In dogs, sensory hairs are found on the muzzle.
Questions and Answers: Small Hair Like Structures Used For Movement Or Sensing Things
What is the primary function of cilia?
Cilia are primarily responsible for generating coordinated movements, often propelling fluids or particles along surfaces.
How do flagella differ from cilia?
Flagella are typically longer and fewer in number than cilia, and they generate a whip-like motion for cell locomotion.
What role do microvilli play in the digestive system?
Microvilli increase the surface area of cells lining the digestive tract, facilitating the absorption of nutrients.
How do stereocilia contribute to hearing?
Stereocilia in the inner ear are involved in the detection of sound vibrations, converting them into electrical signals.
What animals have sensory hairs?
Sensory hairs are found in various animals, including insects, crustaceans, and mammals, where they play roles in touch, proprioception, and other sensory functions.