Electrically neutral in chemistry crossword – Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of electrical neutrality in chemistry, a fundamental concept that governs the behavior of substances and their interactions. As we delve into the intricate world of ions, chemical bonding, and molecular structure, this crossword puzzle guide will unravel the secrets of charge distribution and its profound implications in chemistry.
From the interplay of ions to the intricacies of chemical reactions, we will explore how electrical neutrality shapes the properties of substances and guides their behavior. Join us on this captivating quest to uncover the mysteries of electrical neutrality, one crossword puzzle clue at a time.
Electrical Neutrality Concept: Electrically Neutral In Chemistry Crossword
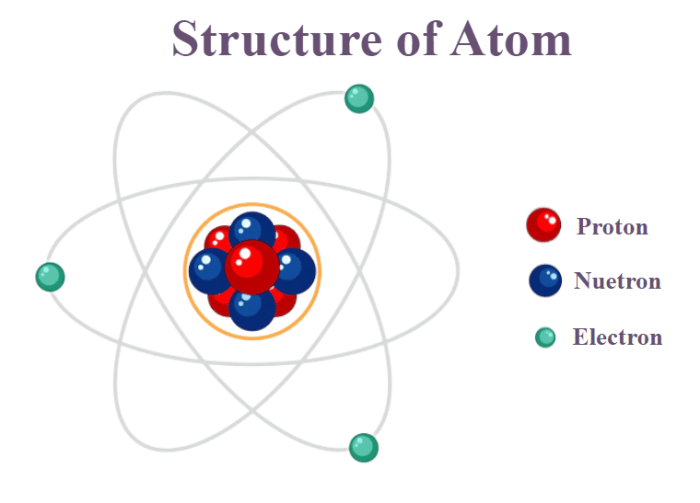
Electrical neutrality in chemistry refers to the absence of net electrical charge in a substance. It implies that the positive and negative charges within the substance are balanced, resulting in an overall neutral state.
Substances that exhibit electrical neutrality include:
- Pure elements, such as sodium, chlorine, and oxygen
- Neutral molecules, such as water (H 2O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), and methane (CH 4)
Ions and Electrical Neutrality
Ions are charged particles that can contribute to the overall electrical charge of a substance. They are formed when atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons.
- Cationsare positively charged ions formed when an atom or molecule loses one or more electrons.
- Anionsare negatively charged ions formed when an atom or molecule gains one or more electrons.
The presence of ions can alter the electrical neutrality of a substance. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) is an ionic compound formed by the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine. Sodium forms Na +cations, while chlorine forms Cl –anions.
The overall charge of NaCl is neutral due to the equal number of positive and negative charges.
Chemical Bonding and Electrical Neutrality, Electrically neutral in chemistry crossword
Chemical bonding plays a crucial role in determining the electrical neutrality of a substance.
Ionic Bonding
Ionic bonding involves the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions. The electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions holds the compound together. Ionic compounds are typically electrically neutral, as the positive charges of cations balance the negative charges of anions.
- Example: Sodium chloride (NaCl) is an ionic compound with Na +cations and Cl –anions. It is electrically neutral due to the equal number of positive and negative charges.
Molecular Structure and Electrical Neutrality
Molecular structure can influence the electrical neutrality of a substance.
Molecular Geometry
The arrangement of atoms within a molecule can create a net electrical charge. Polar molecules have a separation of positive and negative charges due to uneven electron distribution. Nonpolar molecules have a symmetrical electron distribution, resulting in no net electrical charge.
- Example: Water (H 2O) is a polar molecule with a bent shape. The oxygen atom has a partial negative charge, while the hydrogen atoms have partial positive charges.
Bond Polarity
Bond polarity refers to the uneven distribution of electrons in a covalent bond. Polar covalent bonds create a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other. The polarity of bonds can contribute to the overall electrical neutrality of a molecule.
- Example: Hydrogen chloride (HCl) is a polar covalent molecule. The chlorine atom has a partial negative charge, while the hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge.
Electrical Neutrality in Chemical Reactions
Electrical neutrality is maintained in chemical reactions. The total positive charge of the reactants must equal the total positive charge of the products, and the total negative charge of the reactants must equal the total negative charge of the products.
- Example: The combustion of methane (CH 4) with oxygen (O 2) produces carbon dioxide (CO 2) and water (H 2O). The overall reaction is electrically neutral, as the total positive charge of the reactants (4+) is equal to the total positive charge of the products (4+), and the total negative charge of the reactants (4-) is equal to the total negative charge of the products (4-).
Essential FAQs
What is electrical neutrality in chemistry?
Electrical neutrality refers to the state of a substance where the net electric charge is zero, meaning it has an equal number of positive and negative charges.
How do ions contribute to electrical neutrality?
Ions are charged particles that can either be positively or negatively charged. When ions combine, their charges can balance each other out, resulting in an electrically neutral compound.
How does chemical bonding affect electrical neutrality?
Chemical bonding involves the sharing or transfer of electrons between atoms. This can result in the formation of ions or the creation of covalent bonds, both of which can influence the electrical neutrality of a substance.