Embarking on a journey into the realm of atomic structure, this worksheet atomic structure answer key serves as an invaluable guide, illuminating the fundamental concepts that govern the very essence of matter. Delving into the intricacies of protons, neutrons, and electrons, we unravel the secrets of the atomic nucleus and electron cloud, laying the foundation for a comprehensive understanding of the periodic table and atomic number.
Unveiling the significance of electron configuration, this guide empowers you with the knowledge to decipher the chemical properties of elements, unraveling the relationship between electron configuration and the periodic table. Furthermore, we delve into the fascinating world of isotopes and radioactivity, exploring their applications and implications in various fields.
1. Atomic Structure Basics
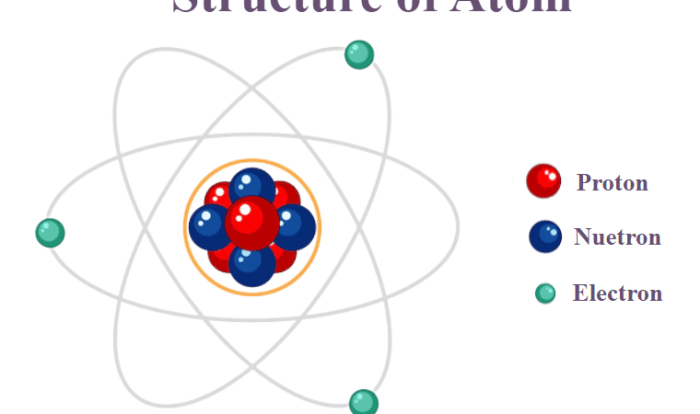
Atomic structure is the fundamental building block of matter. It refers to the arrangement of subatomic particles within an atom, including protons, neutrons, and electrons.
The atomic nucleus is the central core of an atom, containing protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged particles, while neutrons are neutral. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the atomic number of an element, which uniquely identifies it.
Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels called electron clouds. The electron cloud is a region of space where electrons are most likely to be found.
2. Periodic Table and Atomic Number
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
Atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It determines the element’s position in the periodic table and its chemical properties.
For example, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, indicating that it has one proton in its nucleus. Oxygen has an atomic number of 8, indicating that it has eight protons in its nucleus.
3. Electron Configuration: Worksheet Atomic Structure Answer Key
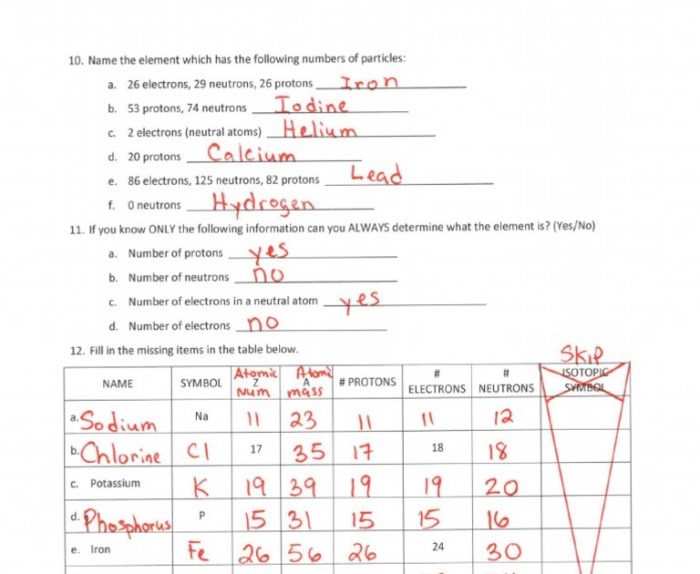
Electron configuration describes the distribution of electrons in an atom’s energy levels. It is crucial for understanding an element’s chemical properties.
To write an electron configuration, follow these steps:
- Determine the atomic number of the element.
- Start filling the energy levels, beginning with the lowest energy level (1s).
- Add two electrons to each energy level until it is full.
- Continue filling the next energy level until all electrons are placed.
For example, the electron configuration of sodium (atomic number 11) is 1s 22s 22p 63s 1.
4. Isotopes and Radioactivity

Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons. They have similar chemical properties but different physical properties.
Radioactivity is the emission of particles or energy from an unstable atomic nucleus. Radioactive isotopes have unstable nuclei and decay over time, emitting particles such as alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays.
Radioactive isotopes have various applications, including:
- Medical imaging (e.g., X-rays, PET scans)
- Cancer treatment (e.g., radiation therapy)
- Radioactive dating (e.g., carbon-14 dating)
5. Applications of Atomic Structure
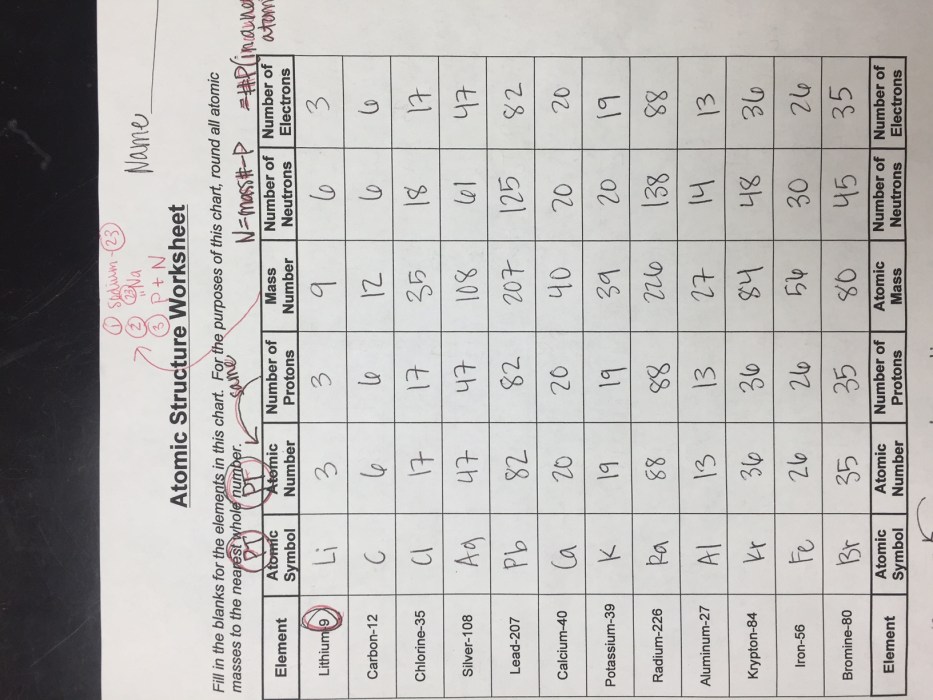
Atomic structure has practical applications in various fields:
Chemistry:Understanding atomic structure helps predict chemical reactions and design new materials with specific properties.
Physics:Atomic structure is essential for understanding the behavior of matter, including nuclear reactions and quantum mechanics.
Medicine:Atomic structure plays a role in medical imaging, radiation therapy, and the development of new drugs.
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of atomic structure?
Atomic structure is the foundation for understanding the properties and behavior of matter. It provides insights into chemical reactions, material properties, and the behavior of elements in various environments.
How does the periodic table relate to atomic structure?
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number, which corresponds to the number of protons in the atomic nucleus. This organization allows for the prediction of chemical properties and trends across different elements.
What are the applications of atomic structure in medicine?
Atomic structure principles are applied in medical imaging techniques such as X-rays and MRI scans. Radioisotopes are used in cancer treatment and diagnosis, providing targeted and effective therapies.