Embark on a captivating journey through the realm of volume and surface area with Unit 11 Volume and Surface Area Homework 3. This comprehensive assignment delves into the fundamental concepts of measuring and calculating the dimensions of three-dimensional objects, equipping you with essential knowledge applicable in diverse fields.
Our exploration begins with an examination of the definitions of volume and surface area, unraveling their significance in quantifying the spatial attributes of objects. We will encounter a diverse array of shapes, each possessing unique volume and surface area characteristics, reinforcing our understanding of these concepts.
Furthermore, we will delve into the units of measurement employed to express volume and surface area, ensuring a solid foundation for accurate calculations.
Volume and Surface Area Definitions: Unit 11 Volume And Surface Area Homework 3
Volume and surface area are two important concepts in geometry that measure the amount of space occupied by an object and the total area of its surfaces, respectively. Volume is a measure of the three-dimensional space within an object, while surface area is a measure of the two-dimensional area of the object’s surfaces.
Objects with different shapes and sizes have different volumes and surface areas. For example, a cube has a volume equal to the cube of its side length, while a sphere has a volume equal to four-thirds times pi times the cube of its radius.
The surface area of a cube is equal to six times the square of its side length, while the surface area of a sphere is equal to four times pi times the square of its radius.
The units of measurement for volume are cubic units, such as cubic centimeters (cm 3) or cubic meters (m 3). The units of measurement for surface area are square units, such as square centimeters (cm 2) or square meters (m 2).
Formulas for Volume and Surface Area, Unit 11 volume and surface area homework 3
The formulas for calculating the volume and surface area of common shapes are as follows:
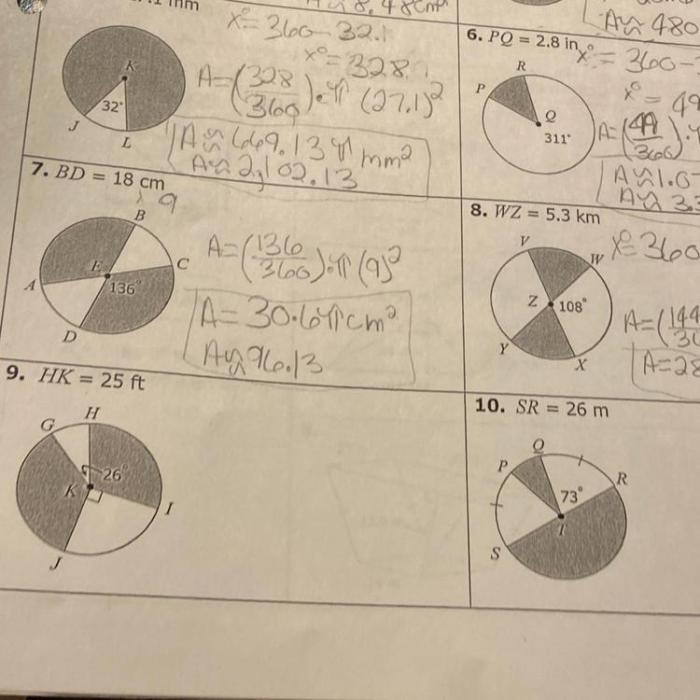
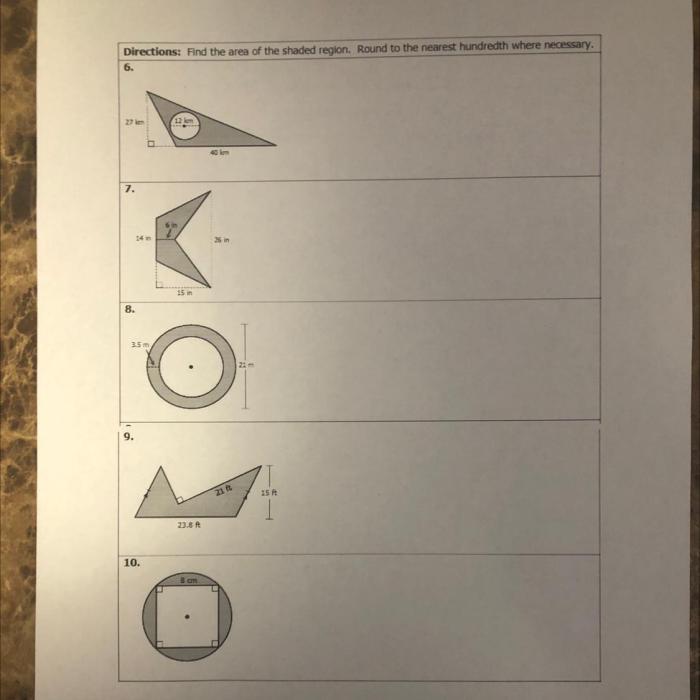
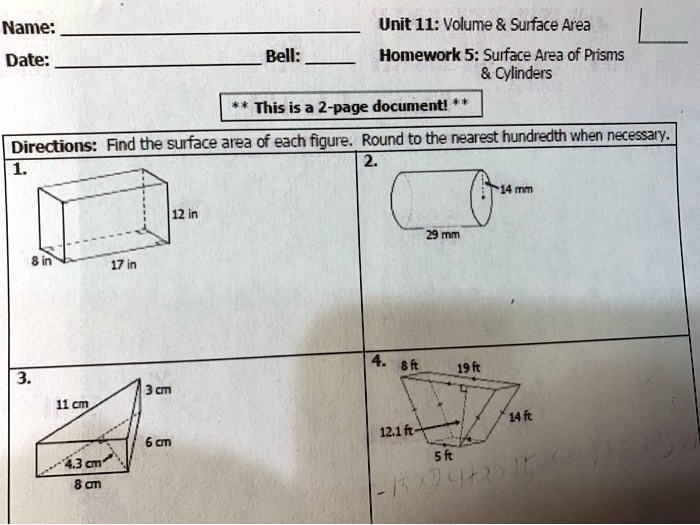
- Cube: Volume = s 3, Surface area = 6s 2
- Sphere: Volume = (4/3)πr 3, Surface area = 4πr 2
- Cone: Volume = (1/3)πr 2h, Surface area = πr 2+ πrs
- Pyramid: Volume = (1/3)Bh, Surface area = Bh + (1/2)Ps
In these formulas, s is the side length of the cube, r is the radius of the sphere or cone, h is the height of the cone or pyramid, B is the area of the base of the pyramid, and P is the perimeter of the base of the pyramid.
Applications of Volume and Surface Area
Volume and surface area have a wide range of applications in real-world situations, including:
- Packaging: The volume of a package determines how much product it can hold, while the surface area determines how much material is needed to make the package.
- Construction: The volume of a building determines how much space it can accommodate, while the surface area determines how much material is needed to build it.
- Medicine: The volume of a patient’s blood determines how much blood they need to receive in a transfusion, while the surface area of their body determines how much medication they need to take.
FAQ Insights
What is the formula for calculating the volume of a cube?
Volume = side length 3
How do I find the surface area of a sphere?
Surface Area = 4πr 2
What are the units of measurement for volume?
Cubic units (e.g., cubic centimeters, cubic meters)