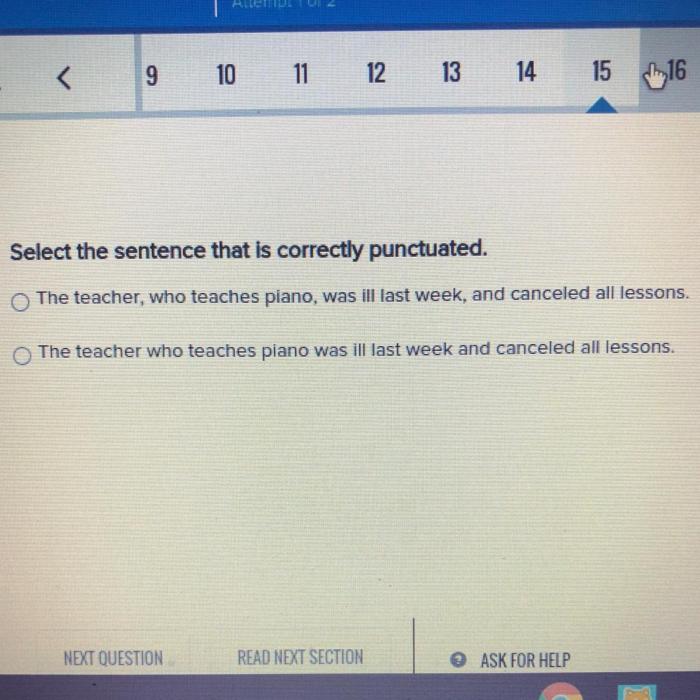
Identify the correctly punctuated sentence – In the realm of written communication, punctuation reigns supreme, orchestrating the flow of ideas and ensuring clarity. This guide delves into the intricacies of punctuation, empowering you to identify correctly punctuated sentences with confidence.
Punctuation, the silent maestro of language, plays a pivotal role in conveying meaning, preventing ambiguity, and enhancing readability. By mastering the art of punctuation, you elevate your writing to new heights, ensuring that your words resonate with precision and impact.
Punctuation Basics
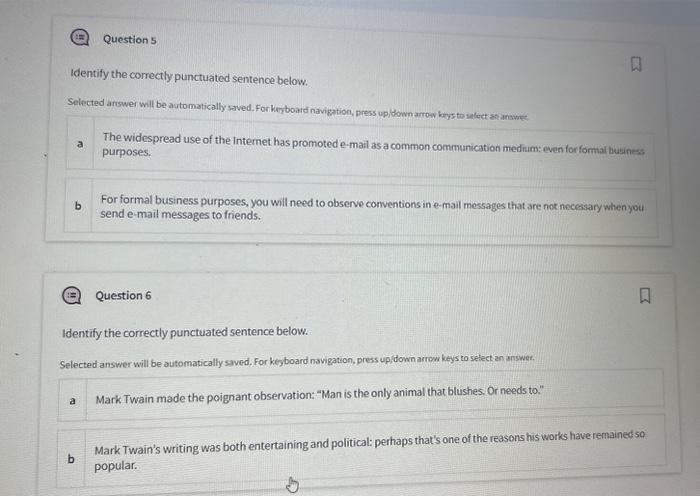
Punctuation is crucial in written communication as it provides clarity, structure, and meaning to sentences. It helps readers understand the intended message by organizing thoughts, indicating pauses, and separating clauses. Without proper punctuation, sentences can become ambiguous, confusing, or even grammatically incorrect.The
most common punctuation marks include the period, comma, semicolon, colon, question mark, exclamation mark, hyphen, and apostrophe. Each mark serves a specific purpose:
- Period (.) indicates the end of a sentence.
- Comma (,) separates items in a list, connects clauses, and sets off introductory elements.
- Semicolon (;) separates independent clauses that are closely related.
- Question mark (?) indicates a question.
- Exclamation mark (!) indicates excitement, surprise, or emphasis.
- Hyphen (-) connects words or parts of words to form compound terms or to indicate a range.
- Apostrophe (‘) indicates possession, omission of letters, or the formation of certain plurals.
Colon (
) introduces a list, quotation, or explanation.
Identifying Correct Punctuation
Identifying correctly punctuated sentences requires attention to key elements:
-
-*Grammatical Structure
Punctuation should align with the grammatical structure of the sentence, separating clauses and phrases as needed.
-*Meaning and Clarity
Punctuation should enhance the meaning of the sentence and make it easy for readers to understand.
-*Conventional Usage
Follow established punctuation rules and conventions to ensure consistency and clarity.
Strategies for analyzing punctuation and identifying errors include:
-
-*Read the sentence aloud
This helps you hear where pauses or separations occur.
-*Check for sentence structure
Identify independent and dependent clauses and use punctuation accordingly.
-*Look for transition words
Words like “and,” “but,” and “however” often indicate the need for a comma or semicolon.
-*Use a punctuation checker
Online tools can help identify potential errors, but they should be used as a supplement to manual checking.
Practice and Examples
Interactive exercises and quizzes can help you practice identifying correct punctuation.Well-punctuated sentences from literature or professional writing provide examples of effective punctuation usage. For instance, in Jane Austen’s “Pride and Prejudice,” the following sentence demonstrates the use of commas to separate items in a list: “She was an active, spirited, feeling young woman, of a warm and affectionate heart.”Punctuation
can also impact dialogue and quotations. For example, the use of quotation marks in the following sentence from “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald indicates a direct quote: “I like large parties. They’re so intimate. At small parties there isn’t any privacy.”
Advanced Punctuation Techniques, Identify the correctly punctuated sentence
Semicolons, colons, and dashes serve advanced punctuation purposes:
- *Semicolons (;) separate independent clauses that are closely related and do not require a conjunction.
- *Dashes (-) set off parenthetical elements or indicate a sudden break in thought.
-*Colons (
) introduce lists, explanations, or quotations.
Commas in complex sentences and lists require careful consideration. For instance, use commas to separate items in a series, but not before the conjunction in a compound sentence.Common punctuation pitfalls include:
-
-*Comma splice
Using a comma to connect two independent clauses.
-*Fused sentence
Writing two independent clauses without any punctuation.
-*Missing commas
Omitting commas where they are necessary.
-*Incorrect use of semicolons
Using semicolons to separate items in a list or to connect unrelated clauses.
Questions Often Asked: Identify The Correctly Punctuated Sentence
What are the key elements to look for when identifying correctly punctuated sentences?
When analyzing punctuation, pay close attention to the placement of commas, periods, semicolons, and other punctuation marks. Ensure that they are used correctly to separate clauses, phrases, and words, and that they adhere to the rules of grammar and style.
How can I improve my punctuation skills?
Regular practice is key to mastering punctuation. Engage in writing exercises, proofread your work carefully, and study examples of well-punctuated writing. Additionally, consult style guides and grammar resources for guidance.
What are some common punctuation errors?
Common punctuation errors include comma splices, misplaced apostrophes, incorrect use of quotation marks, and dangling modifiers. Familiarize yourself with these errors and their corrections to avoid them in your writing.