Rank the following base pairs according to their stability. – In the realm of molecular biology, understanding the stability of base pairs is paramount. Base pair stability plays a pivotal role in DNA and RNA structure, gene expression, and genetic stability. This guide delves into the factors that influence base pair stability, establishes ranking criteria, and provides a comprehensive ranking of common base pairs.
By exploring these concepts, we gain insights into the intricate workings of genetic material and its implications for various biological processes.
The stability of base pairs is influenced by a multitude of factors, including hydrogen bonding, stacking interactions, and base composition. These factors contribute to the overall stability of the double helix and affect the melting temperature, free energy, and enthalpy of base pairs.
1. Base Pair Stability Factors
The stability of base pairs is influenced by several factors, including:
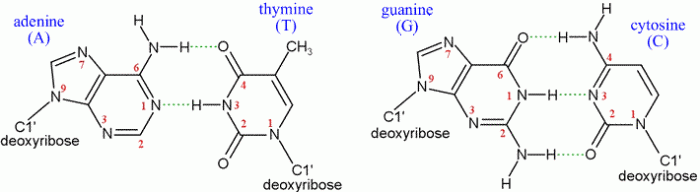
- Hydrogen bonding:Base pairs are formed by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. The number of hydrogen bonds between a pair of bases determines its stability. GC base pairs form three hydrogen bonds, while AT base pairs form two.
- Stacking interactions:Base pairs stack on top of each other, forming a stable structure. The stacking interactions between adjacent base pairs contribute to the overall stability of the double helix.
- Base composition:The overall base composition of a DNA molecule can also affect base pair stability. DNA molecules with a higher GC content are generally more stable than those with a higher AT content.
2. Base Pair Ranking Criteria
Base pairs can be ranked according to their stability based on several criteria, including:
- Melting temperature (Tm):The Tm is the temperature at which half of the base pairs in a DNA molecule have melted. A higher Tm indicates a more stable base pair.
- Free energy:The free energy of a base pair is a measure of its thermodynamic stability. A lower free energy indicates a more stable base pair.
- Enthalpy:The enthalpy of a base pair is a measure of the heat absorbed or released when the base pair is formed. A lower enthalpy indicates a more stable base pair.
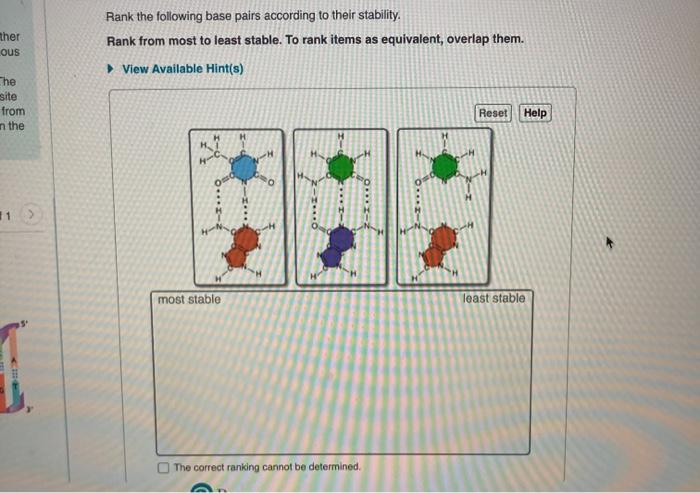
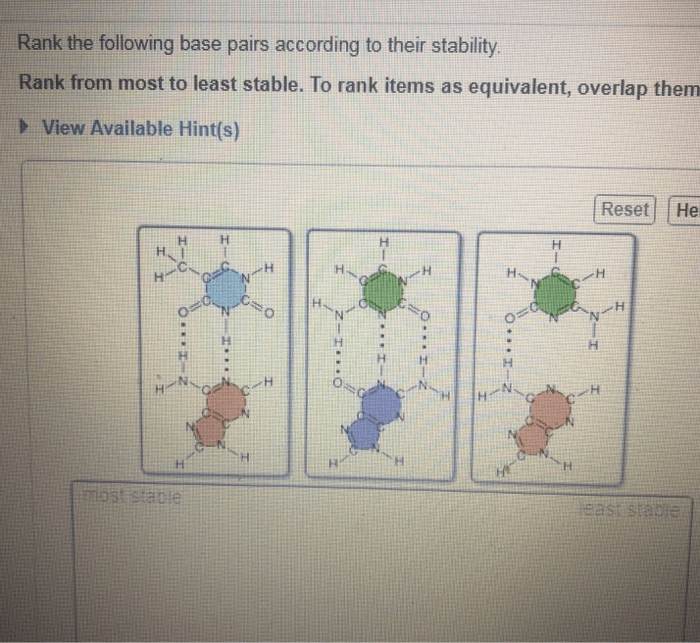
3. Base Pair Ranking
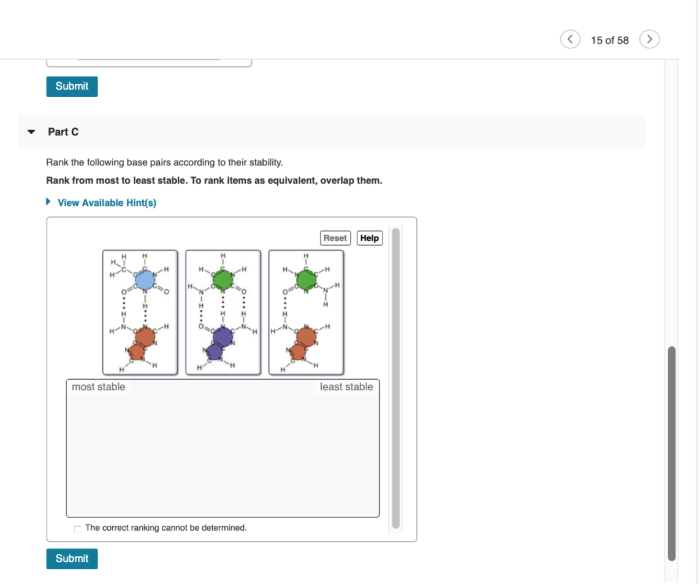
Based on the stability criteria discussed above, the following base pairs can be ranked as follows, from most stable to least stable:
- GC
- AT
- AU
- GU
GC base pairs are the most stable because they form three hydrogen bonds and have a high stacking energy. AT base pairs are less stable because they form only two hydrogen bonds and have a lower stacking energy. AU and GU base pairs are the least stable because they form only one hydrogen bond and have a low stacking energy.
4. Stability Comparisons
The stability of base pairs can vary under different conditions, such as temperature, pH, and ionic strength.
- Temperature:The stability of base pairs decreases with increasing temperature. This is because the heat energy causes the base pairs to break apart.
- pH:The stability of base pairs is also affected by pH. Acidic conditions can cause the protonation of the nitrogenous bases, which can disrupt the hydrogen bonding between the bases.
- Ionic strength:The stability of base pairs is decreased by high ionic strength. This is because the ions can compete with the hydrogen ions for binding to the nitrogenous bases.
5. Applications of Base Pair Stability Ranking
The ranking of base pairs according to their stability has several practical applications in molecular biology, genetics, and biotechnology.
- DNA melting and annealing:The stability of base pairs is used to control the melting and annealing of DNA molecules. This is important for techniques such as PCR and DNA sequencing.
- Gene expression:The stability of base pairs is also important for gene expression. The stability of the base pairs in the promoter region of a gene can affect the rate of transcription.
- Drug design:The stability of base pairs is also used in drug design. Drugs can be designed to bind to specific DNA sequences by targeting the stability of the base pairs in those sequences.
Popular Questions: Rank The Following Base Pairs According To Their Stability.
What factors contribute to base pair stability?
Factors such as hydrogen bonding, stacking interactions, and base composition influence the stability of base pairs.
How are base pairs ranked according to stability?
Base pairs are ranked based on parameters such as melting temperature, free energy, and enthalpy.
What are the applications of ranking base pairs according to stability?
Ranking base pairs according to stability has applications in molecular biology, genetics, and biotechnology, aiding in the design and manipulation of DNA and RNA molecules.